Cancer is a well-known disease for its mysterious occurrences and incurability. Recent researches have revealed many facets (sides) of cancer, its biology of action and treatment.
Hippocrates in 2300 BC observed a breast tumor which was like limbs of crabs and hence he named the disease as karkinoma in Greek.
Later it was named Cancer according to Latin. Cancer is not a single unit of disease rather than a multiple / different set of diseases (more than 100) combined together causing an imbalance in normal functioning of human beings in physiological, psychological and has great difficulties in maintaining societal relationships and wellbeing.
In simple terms, cancer is a disease caused by the rapid multiplication (proliferation) of any body cells without control or regulators leading to formation of group of cells similar in origin and without any restriction to multiply.
This nature of parasite host relationship exhibited by one’s own cells forming a mass of cells called tumor becomes invasive and malignant causing imbalances.
When matured tumor cells travels along the blood stream and reach other body part, they develop cancer tissues at those places, this stage is known as metastases.
Broadly, cancer can be differentiated into Carcinoma, Sarcoma, Leukemia, Lymphoma, Myeloma etc., But cancers are mainly indicated by the organs in which it develops almost all the organs exhibited their cancerous properties.
Some of the types are: Bladder cancer, Brain and Nervous System Cancer, Breast Cancer, Cervical Cancer, Colorectal Cancer, Esophageal Cancer, Gastric Cancer, Head and Neck Cancer, Sarcoma, Kidney Cancer, Liver Cancer, Leukemia, Lung Cancer, Lymphoma, Melanoma, Myeloma, Ovarian Cancer, Pancreatic Cancer, Prostate Cancer and so on.
What is Breast Cancer?
An uncontrolled cell growth in breast cells can be generally termed as breast cancer. Out of all types of cancer; Breast Cancer is more prevalent in women above the age of 40 and are seen rarely in age below 40.
Breast Cancer is not confined only to women, men also can have breast cancer.
At early stages the cancer is not fatal and a person with breast cancer can behave normally but at later stages when they reach Metastases, the disease may not be curable and it becomes fatal.
Survivors of metastases are very few and their malignancy is under control which means they are constantly under medication.
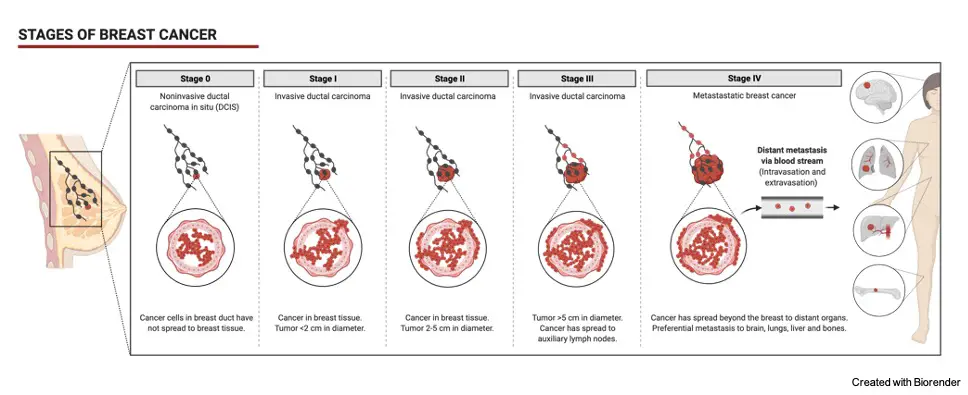
Stages of Breast Cancer
Breast Cancer is divided into stages based on the severity and spread. The main method employed here is the TNM method which was accepted by Union for International Cancer Control and American Joint Committee on Cancer.
T – Tumor – initial tumor stage can or cannot be a cancer
N – Node – Tumor Spread to Lymph Nodes
M – Metastasis – A tumor stage when it reaches other body parts
Further, the TNM stage is differentiated into Clinical and Pathological stages. The clinical stage classification is staging the tumor during diagnosis.
Pathological Stage classification is staging after surgery. Along with this AJCC also included tumor grade, estrogen – progesterone receptor status and HER2 protein status
Causes of Breast Cancer
Earlier, the reasons for cancer was unknown and remained mysterious. The advancements in research techniques and knowledge on cell and molecular biology developed a new perspective of cancer and treatments to cure or control the cancer.
Main reason for cancer is uncontrolled cell proliferation which is induced by external or internal factors.
The internal factors are governed by the cells and its functions. In Breast Cancer, the internal factors can be Hormonal or genetic mutations or acquired mutation.
Specifically, two cell types are prone to become malignant in breast. They are: duct cells and lobules.
Lobules are milk secreting gland, milk secreted is travelled to the duct to the nipple.
Duct cells lines the duct which collects many lobules and secrete milk to the young ones.
External factors account to exposure to particular radiations or drugs which causes cancer. But external factors causing breast cancer are still unknown.
In other terms, Breast Cancer can be Inherited or Acquired. When inherited, gene mutations run throughout the family is passed on to younger generation there by causing Breast Cancer.
In this case, acquiring cancer at earlier or later stages is inevitable. The Tumor suppressor genes or proto – oncogenes are mutated to produce oncogenes.
Genes responsible for Progesterone or Estrogen receptors are activated all over the cancerous cells inducing elevated cell growth.
Acquired can be of external environmental factors, behavioral factors or exposure to radiations and cancer inducing drugs.
Exposure to external factors causes similar gene mutations in cells causing proliferations.
Generally, our body itself has 3 mechanisms to keep the cell cycle in check and prevent all the organs or any part of the body from tumors.
They are: DNA Repair System, Apoptosis and Telomeres. The repair systems are governed or maintained by internal or environmental factors and any errors corresponding to the cell cycle will accumulate over a long period of time and causes tumor further develops into malignant disease.
The internal or external environmental factors induces certain genes namely proto – oncogenes (encourages cell division) and tumor suppressor genes (inhibits cell division).
When mutation occur, the proto – oncogenes becomes oncogenes and cause abnormal cell division. The cell division exceeds any limitation causing cancer.
Oxidative Phosphorylation: Definition, Function, Significance, and Facts
Metastatic Breast Cancer
Metastatic Breast Cancer can be categorized into;
1. Metastatic Invasive
Cancerous cells start multiplying here and then proceeds further to regions surrounding it and then its metastases (i. e) they spread to different organs through blood stream.
1. Invasive Ductal Carcinoma: proliferation in ducts
2. Invasive Lobular Carcinoma: cancerous outgrowth from lobules
3. Inflammatory Breast Cancer: A quick growing cancer type which initiates either from duct or lobule and spreads to different regions at a rapid rate
4. Paget’s disease of Breast: Specialized Paget cells are formed in areola surrounding the nipple
5. Angiosarcoma: Cancerous cells forming around the lining of lymph vessels
6. Phyllodes Tumors: cell proliferation in connective tissues of breast.
2. Non – Invasive
This type of cancerous growth is restricted only to certain affected regions and does not spread. This is indicated as Stage 0 breast cancer.
With proper care and medication this can be controlled. If any outbreaks take place in the tumor cells non – invasive can transform to Metastatic Invasive type and proceed to next stages. The types are:
1. Ductal Carcinoma in situ
2. Lobular Carcinoma in situ
Symptoms of Breast Cancer
1. Reddening of skin – Rash formation
2. Breast skin becomes flaky
3. Uneven size of the breast
4. Lymph nodes in armpits and region surrounding breast becomes swollen
5. When metastasis spread to brain it causes dizziness and loss of steady state of mind
6. Bones may pain
7. Nausea
8. Swelling of organs where the tumor is spread.
Treatment of Breast Cancer
1. General treatments include surgical removal of breast, radiation therapy, chemotherapy and symptom-based treatment to suppress the symptom and maintain control.
2. Specific treatment includes target specific treatment where the reason for cancer is determined and targeted to cure particular gene or hormone function.
If HER 2 Protein is the reason for cancer then therapies to suppress HER 2 protein is used.
If BRCA 2 genes are mutated their expressions are inhibited by certain specific therapy. These therapies are not the same for all as they are dependent on the severity and extent of disease.
Breast Cancer Citations
- Breast Cancer: Current Perspectives on the Disease Status. Adv Exp Med Biol . 2019;1152:51-64.
- Primary and secondary prevention of breast cancer. Ann Agric Environ Med . 2017 Dec 23;24(4):549-553.