Nucleotide: Definition, Meaning, & Examples
Table of Contents Nucleotide Definition A nucleotide is the basic building block of nucleic acid. Examples of a nucleic acid include DNA and RNA. Nucleic acids are one of the…
Table of Contents Nucleotide Definition A nucleotide is the basic building block of nucleic acid. Examples of a nucleic acid include DNA and RNA. Nucleic acids are one of the…
Terrestrial Animals Definition Terrestrial animals reside, grows, and reproduce on land. An ecological environment inhabited by a certain species is called a habitat. There are different types of habitats depending…
Table of Contents Evolution Definition Change in the genetic composition of a population over successive generations is termed Evolution. It is also defined as progressive change. What is Evolution? Interaction…
Opsonization Definition The process of binding opsonins to the surface of the antigen is called opsonization. Opsonization occurs to readily identify the antigen that can be engulfed by phagocytes for…
Table of Contents Xylem Definition Xylem is a type of plant tissue which is used to transfer water and nutrients. Xylem is commonly found in higher plants. The plants consisting…
Table of Contents Ganglia Definition In biology, ganglia is an oval-shaped structure that contains the cell bodies of a neuron. It is also called an encapsulated collection of bodies of…
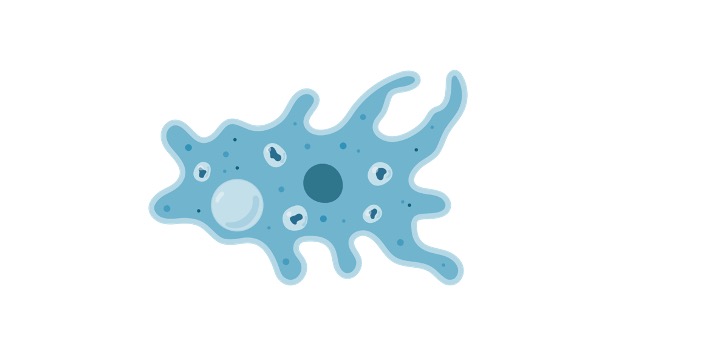
Table of Contents Pseudopodia Definition A temporary projection of the cytoplasm is referred to as a pseudopodium. They resemble an arm is filled with the cytoplasm and contains cytoskeleton filaments.…
Radial Symmetry Definition When the body plan of any organism is divisible into two identical parts around the central axis, the form of symmetry is called radial symmetry. In biology,…
Labia Definition Labia is the female’s genital part, which consist of vulva, which is the external area. In humans, there are two parts of labia, which are labia majora and…
Table of Contents Antagonistic Muscle Definition The word antagonistic means working opposite or the primary doer. Thus, antagonism is defined as an action or substance that can prevent the physiological…