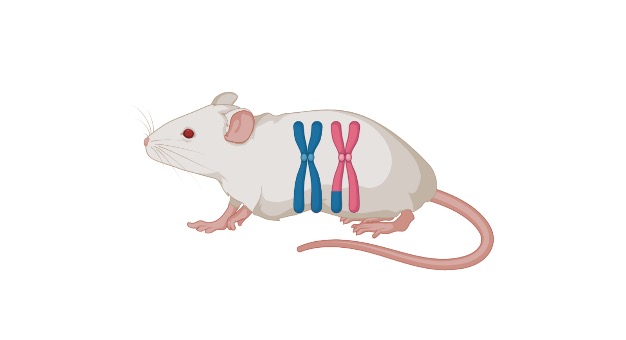
Heterozygous Definition
An organism containing two different alleles for a particular trait is called heterozygous.
Generally, a cell, a nucleus, or an individual organism that contains non-identical alleles for a particular trait is termed heterozygous. In the heterozygous organism, two different alleles are present at the same loci on homozygous chromosomes. For example- an allele that code for the same trait such as eye color has two dissimilar code such as black and brown whereas, in homozygous condition, both the alleles are identical and have similar genes for a particular trait.
Diploid is the condition where an organism consists of two sets of chromosomes. The diploid chromosome inherits one of the chromosomes from the mother and another one from the father. Based on their loci, the maternal chromosome match with its corresponding paternal gene.
The heterozygous is described as the chromosome that bears the same alleles in the loci of matching chromosomes. The heterozygous chromosome is consists of two dissimilar alleles from which one allele is dominant and the other is recessive. Based on “Mendel’s law of Dominance” the dominant allele will be expressed in the phenotype of the organism.
Heterozygous Citations
Share
Related Post

11 Postdoctoral Jobs at Delft University of Technology (TU Delft), Netherlands
If you’re a PhD degree holder and seeking postdoctoral fellowships, Delft University of Technology

09 Fully Funded PhD Programs at University of Antwerp, Belgium
If you’re a Masters degree holder and seeking Fully Funded PhD Programs, University of

11 Postdoctoral Jobs at University of Arizona, Arizona
If you’re a PhD degree holder and seeking postdoctoral fellowships, University of Arizona, Arizona

03 Fully Funded PhD Programs at Vlaams Instituut voor Biotechnologie, Belgium
If you’re a Masters degree holder and seeking Fully Funded PhD Programs, Vlaams Instituut

09 Postdoctoral Jobs at University of California, Los Angeles, California
If you’re a PhD degree holder and seeking postdoctoral fellowships, University of California, Los

04 Fully Funded PhD Programs at Umeå University, Umeå, Sweden
If you’re a Masters degree holder and seeking Fully Funded PhD Programs, Umeå University,

11 Postdoctoral Jobs at Delft University of Technology (TU Delft), Netherlands
If you’re a PhD degree holder and seeking postdoctoral fellowships, Delft University of Technology

09 Fully Funded PhD Programs at University of Antwerp, Belgium
If you’re a Masters degree holder and seeking Fully Funded PhD Programs, University of

11 Postdoctoral Jobs at University of Arizona, Arizona
If you’re a PhD degree holder and seeking postdoctoral fellowships, University of Arizona, Arizona

03 Fully Funded PhD Programs at Vlaams Instituut voor Biotechnologie, Belgium
If you’re a Masters degree holder and seeking Fully Funded PhD Programs, Vlaams Instituut

09 Postdoctoral Jobs at University of California, Los Angeles, California
If you’re a PhD degree holder and seeking postdoctoral fellowships, University of California, Los

04 Fully Funded PhD Programs at Umeå University, Umeå, Sweden
If you’re a Masters degree holder and seeking Fully Funded PhD Programs, Umeå University,