What is Krebs Cycle?
Tricarboxylic cycle or Krebs cycle is the part of cellular respiration, the series of reaction takes place in matrix of mitochondria to generate energy (ATP) under aerobic condition.
It produces intermediates used in several biosynthetic pathways in living beings.
TCA cycle has been discovered by Hans Kreb in 1937.
Plants mitochondria generates essential energy for various cellular processes, via TCA cycle and ETC (electron transport chain).
Oxidation of organic acid produce reducing equivalents which transferred to etctron transfer chain and via set of reactions ATP formation takes place following ADP phosporylation.
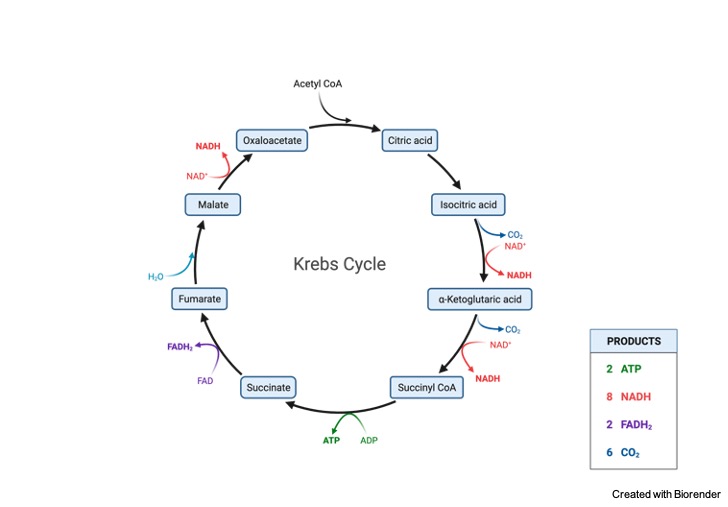
Krebs Cycle Steps
There are eight steps are involved in Krebs cycle.
Step 1: In this step acetyl CoA binds with oxaloacetate (four carbon compound)and produce citrate ( Six carbon compound) while releasing co-enzyme A, reaction is catalyzed by citrate synthase.
Step 2: Citrate is converted to isocitrate in the presence of acotinase enzyme, it releases a water molecule.
Step 3: Isocitrate is converted to alpha ketoglutarate (Five carbon) in the presence of isocitrate dehydrogenase. This chemical reaction generate NADH from NAD and removes carbon dioxide molecule.
Step 4: Oxidation of alpha ketoglutarate produces succinyl Co-A( Four carbon) in the presence of alpha ketoglutarate dehydrogenase, in this reaction reduction of NAD+ to NADH is encountered.
Step 5: Succinate is formed by enzymatic conversion of succinyl CoA. A GTP is formed during reaction. The enzyme succinyl Co-A participates in the reaction.
Step 6: Oxidation of succinate leads to the formation of fumarate, FADH2 is formed in this reaction reaction is catalyzed by succinate dehydrogenase.
Step 7: Hydration of fumarate to malate is catalysed by fumarate hydratase.
Step 8: Oxidation of malate is catalysed by malate dehydrogenase and results into the formation of oxaloacetate.
Mitochondria: Function, Definition, Significance, and Facts
Outcome of Krebs Cycle
Cycle produces following compounds in each turn;
• Carbon dioxide (two molecules)
• Hydrogen ion (three)
• NADH (three molecules)
• GTP (one molecule )
• FADH2 (one molecule)
ATP Generation in Krebs Cycle
1. 3 NAD+ = 9ATP
2. 1 FAD = 2 ATP
3. 1 GTP = 1 ATP
Importance of Krebs Cycle
• Synthesis of biomolecules like nucleotides , cytochrome, amino acide etc is derived from the intermediate compounds synthesized during Krebs cycle.
• Succinyl Co-A is a precursor of chlorophyll synthesis.
• Alpha ketoglutarate, pyruvic acid participates in the synthesis of several amino acids.
• ATP generated by Krebs cycle are utilized in many cellular metabolic activity.
• This cycle provides carbon skeleton useful for the maintenance and growth of healthy cells.
• Krebs cycle has a key role in lipogenesis and gluconeogenesis.
• Amount of NAD+ and ATP regulates the occurrence of cycle.
Krebs Cycle Citations
- Krebs Cycle Reimagined: The Emerging Roles of Succinate and Itaconate as Signal Transducers. Cell . 2018 Aug 9;174(4):780-784.
- The Kreb Uric Acid Cycle: A Forgotten Krebs Cycle. Trends Biochem Sci . 2018 Nov;43(11):847-849.