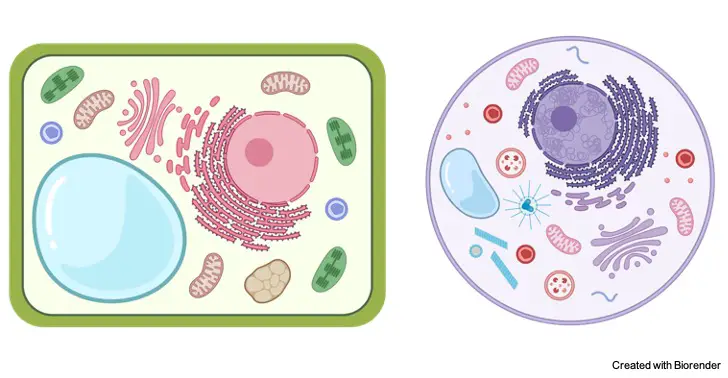
What is Cytoplasm?
The term cell cytoplasm is introduced by a swiss biologist named Rudolf von Kölliker in 1863 almost 198 years later than the discovery of cells by Robert hook.
Definition of Cytoplasm
In simple words, the cytoplasm or cytosol is a fluid that fills the interior of cells.
Although, the latest studies suggested that cytoplasm is not an ordinary fluid-like structure but similar to liquids that form glass.
Eukaryotic Cytoplasm
Most of the volume in eukaryotic cells is occupy by cytoplasm, this gel-like, water-based moving fluid contains various cellular organelles responsible for function necessary for the survival of the cell.
The cytoplasm consists of salts and many enzymes that perform peculiar chemical reactions inside the cell.
Electron microscopy shows that cytoplasm comprises slender strands of three-dimensional lattice made up of various cytoplasmic proteins bearing scaffolds.
Cytoplasm can be viewed under a microscope through the staining technique.
Krebs Cycle: Definition, Diagram, Steps, and Mechanism
Prokaryotic Cytoplasm
As prokaryotes such as bacteria lack functional segregation, cytoplasm of bacteria represents everything inside the even genetic material of the bacteria is also dispersed in cytoplasm except the cytoplasm bounded by two membranes called periplasm in gram-negative bacteria.
Bacterial cytoplasm appears transparent under the light microscope but higher resolution electron microscopy shows the granular structure of cytoplasm.
Cytoplasmic inclusions related to the nutrient storing sites are also found in the cytoplasm of some bacteria.
Although prokaryotic cytoplasm is similar to eukaryotic in composition bacterial cytoplasm tends to be more like gel with the exceptional quality of flow with enables the movement of molecules inside the bacteria as well as into and out of bacteria.
Calvin Cycle: Definition, Diagram, Mechanism, and Steps
Function of Cytoplasm
Cells maintained their shape due to the turgidity provided by cytoplasm.
In eukaryotic cells, most of the cellular organelles such as ribosomes, mitochondria, golgi apparatus, endoplasmic reticulum, lysosomes reside in cytoplasm thus it is the site for all chemical reactions to occur.
The cytoplasm also assists in metabolic activities.
Due to gel like nature cytoplasm offer fluidity to cell
Difference Between Cytoplasm and Protoplasm
Protoplasm constituents cytoplasm, nucleus, and all other living components of the cell, it can be said that the cellular components of cells are considered as protoplasm while gel like fluid filled inside cell membrane is called cytoplasm.
Cytoplasm Citations
- Cytoplasm’s Got Moves. Dev Cell . 2021 Jan 25;56(2):213-226.
- How crowded is the cytoplasm? Cell . 1982 Sep;30(2):345-7.