Table of Contents
DNA Structure Definition
Chromosomes present in the nucleus of a cell determine the structure, type, and functions of a cell. The chromosome is made up of deoxyribonucleic acid or DNA. All of the characteristics of an organism are determined by DNA, which is considered as genetic material and contains all the genetic information. The information is passed on to every generation and offspring inherit the information from their parents.
DNA Structure and Nucleotides
DNA is comprised of a double-helical structure and intertwined spirals with one another continuously bending on itself. The spirals never get closer or further away. A nucleotide is a monomeric unit of DNA that is comprised of nitrogenous bases adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine. The possible permutations of these nucleotide pairs make a person unique.
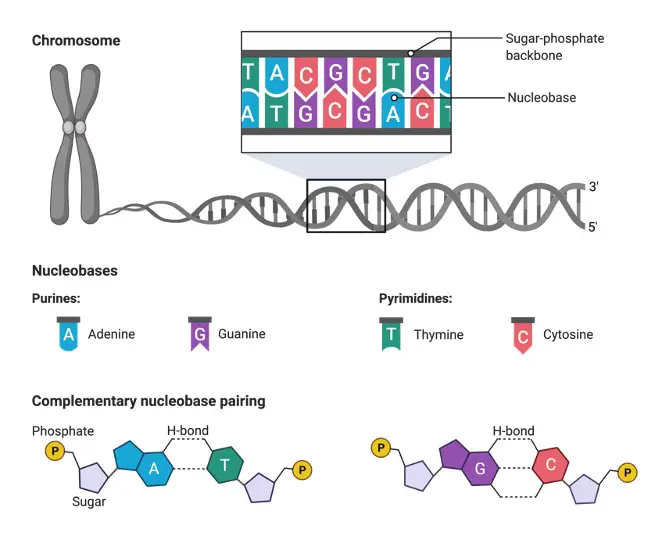
In the double helix nature of DNA, the nucleotides are situated in adjacent pairs. The nucleotide pairing takes place by following some rules, such as-
• The nucleotide is of four types, adenine, cytosine, guanine, and thymine.
• Thymine only pairs with adenine.
• Guanine can only pair with cytosine.
Therefore, thymine would not pair with cytosine similarly guanine would not pair with adenine. The nucleotide sequences determine the structure, anatomical and physical features of an organism.
DNA Replication
Cells pass their genetic information into their offspring or daughter cells. Therefore they replicate their genetic material, i.e. DNA. The genes (fragments of DNA) are also copied to code for particular bodily functions. DNA should be replicated exactly in the process of DNA replication. The process requires some essential things-
• Template (actual DNA or parent DNA)
• Freely available nucleotide pool
• Essential enzymes to catalyze the reaction
• Energy (ATP)
The replication starts with uncoiling of the double-helical structure so that the nucleotides are freely available for pairing. After pairing all the nucleotides in the template, the structure again re-coil into its original double-helical structure. As a result, replication of two strands produces 2 copies of each strand and overall produces 2 DNA copies. Replication is considered a semi-conservative process.
This is because it only inherits 50% of the genetic material from parent DNA and the other 50% is newly formed. This template technique allows genetic information to pass from generation to generation.
DNA Structure Citations
- Insights into the Structure and Energy of DNA Nanoassemblies. Molecules . 2020 Nov 24;25(23):5466.
- The birth and development of the DNA theory of inheritance: sixty years since the discovery of the structure of DNA. J Genet . 2014 Apr;93(1):293-302.
- DNA structure and function. FEBS J . 2015 Jun;282(12):2279-95.
- Figures are created with BioRender.com







